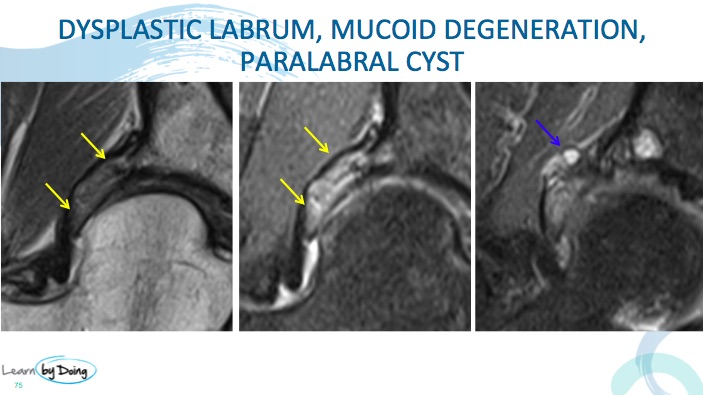
A dysplastic acetabular labrum is most commonly seen when there is an underlying dysplasia of the hip with undercoverage of the femoral head by the acetabulum. The labrum elongates and enlarges. A simplified way to think about it would be that the labrum elongates and hypertrophies to compensate for the lack of coverage of the femoral head by the acetabulum. There is no measurement for what is a a normal size of the labrum, rather, having a sense of what a normal sized labrum should look like is important when deciding if the labrum is enlarged or not. Because its dysplastic, the labrum is then more prone to mucoid degeneration and tearing.
 Image Above: Normal size of labrum in different patients.
Image Above: Normal size of labrum in different patients.
Image Above: Normal acetabular coverage ( image on left) and undercoverage on right. Angles ( such as the Centre Edge Angle) can be measured to assess for acetabular dysplasia but often having a sense of what looks like undercoverage on a plain xray like the image above can be a good indicator that the labrum may be elongated and dysplastic.